

The discovery of X-ray is one of the most important medical achievements that has led to the diagnosis of many human diseases. Despite the benefits of radiation, one should be aware of the dangers of radiation and avoid excessive exposure to this radiation.
The amount of radiation generated by radioactive materials from industrial processes and X-ray exposures account for half of all human-absorbed radiation. Excessive radiation can destroy cells and alter the structure of human DNA.
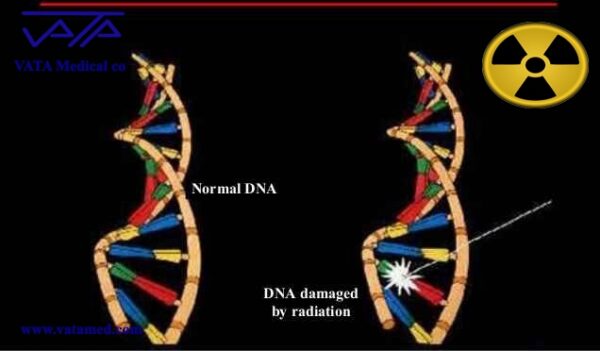
Continuous exposure to X-rays, absorption of higher doses such as CT and interventional procedures in some cases lead to biological effects on the body. Higher absorbed dose means higher risk. The relationship between these effects is almost linear.
Side effects at high doses can include redness of the skin, infertility, cataracts and hair loss. Patients undergoing interventional surgery who require fluoroscopy, which lasts an hour or more, may rarely experience radiation-induced skin damage .
Possible effects of X-rays, also known as delayed effects, include genetic effects and cancer, which can occur years after receiving radiation.
The biological effects of X-rays are related to the following factors:
1- Type of received radiation:
Rotating X-ray obtained by CT scan that takes three-dimensional images of the patient’s body has a higher dose and higher risk than X-rays of radiological devices that take instantaneous images.
2- The amount of radiation received:
The amount of radiation received is directly related to the exposure time of people. This risk increases with the dose and the number of repetitions of the imaging. For example, in fluoroscopic imaging, the minimum time a person is exposed to radiation is 20 minutes, which imposes a dose equivalent to 20 millisieverts.
3- The part of the body that is irradiated:
Although a person should have a complete protective cover against radiation, but the most effects of X-rays on the thyroid gland, testicles and ovaries, as well as the iris of the eye due to cell proliferative effects It’s fast.
4 – Age of children:
Children are more affected by X-rays than adults and also women than men
5- Genetic characteristics of people:
People with higher levels of health have more immunity to the effects of radiation.
Pregnant mothers should be less exposed to radiation, and if a pregnancy is likely to occur in the first few months of fetal development, inform the radiologist and use lead shields. Excessive exposure of pregnant women to radiation will impair the growth and function of the fetus and the birth of low birth weight children.
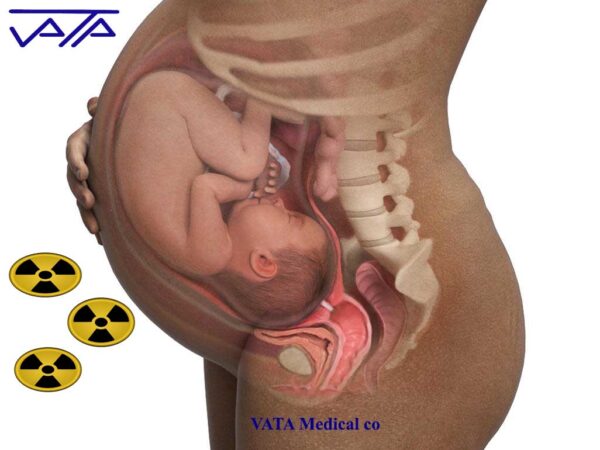
x-ray radiation risks and pregnancy
Important parts of a child’s body, such as the thyroid gland, testicles, and ovaries, should be protected by lead shields to prevent biological damage due to their active proliferating cells.

x-ray radiation risks to children
The dose received is measured in millisieverts (msv).
The dose received by each part of the body in the radiographic process is shown in the table below:
Dental radiography 0.01 millisievert
Chest radiograph 0.1 millisievert
chest scan 10 millisievert
risk of cancer 100 millisievert
Death 10,000 millisieverts
In an article entitled X-Ray radiation protection methods, the method of preventing the effects of radiation is completely discussed, but in short, the following strategies should be used to prevent the harmful effects of X-rays for patients and staff:
1- Imaging center rooms should be equipped with high purity lead to prevent radiation leakage.
2- Considering the three principles of X-ray exposure time, distance from the radiation source and radiation protection
2- Limiting the imaging area to the part of the body that needs radiation
3- Using lead shields (x-ray protection apron , thyroid x-ray shield , gonad x-ray shield )
4- Using the highest kV and the lowest mA during radiology
5- Reducing the reproducibility of radiology by keeping the patient’s limb fixed
According to the mentioned cases, radiology technicians during radiology should be located in control rooms equipped with lead, and if for any reason they are outside the control room, they should be equipped with lead cover and shields (lead cover, lead thyroid, lead gonad) ) To turn. They should also consider the placement of lead shields during radiology as well as the amount of radiation needed for the patient.